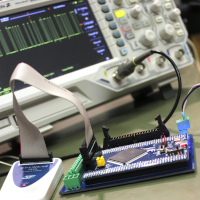
Prototyping - esential for product development
 Prototyping is one of the key stages in product design and development. Prototyping allows
functional testing of the device, analysis of parameters, and corrective
actions if necessary, thus preparing for the mass production phase of the product and significantly
reducing the costs that may be required for unforeseen product modifications in the future.
Prototyping is one of the key stages in product design and development. Prototyping allows
functional testing of the device, analysis of parameters, and corrective
actions if necessary, thus preparing for the mass production phase of the product and significantly
reducing the costs that may be required for unforeseen product modifications in the future.
During prototyping
- Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are manufactured, surface mount and through-hole components are mounted, firmware is flashed into the microcontroller
- If necessary, design, manufacture and assembly of mechanical structures are performed
- The connection of individual electronic embedded systems and mechanical assemblies (mechatronics) into the final product is performed
- Comprehensive functional, stress testing and tuning of the device, analysis of operating mode and parameters are being carried out
Lifecycle managment
The product life cycle does not end with the design or prototyping stage. Engineering lifecycle managment is applied during which further steps related to the reduction of production costs and potential threats of the facility are taken.
Design for manufacturing
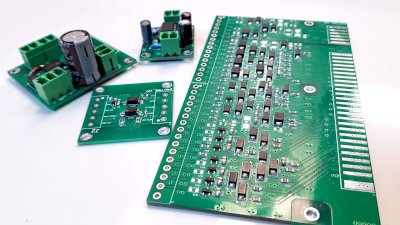 The goal of the Design For Manufacturing (DFM) process is to reduce the cost of mass production of
the entire system or its separate components.
The goal of the Design For Manufacturing (DFM) process is to reduce the cost of mass production of
the entire system or its separate components.
During optimisation
- Specific corrections for printed circuit boards are made to facilitate the automated board assembly process
- Optimal surface mount (SMD) and through hole (THT) components and their positions are selected
- Alternatives for the complexity and arrangement of peripheral elements in the final product are evaluated
- The production process of mechanical structural elements and materials used are evaluated, alternatives are proposed
Alternative solutions
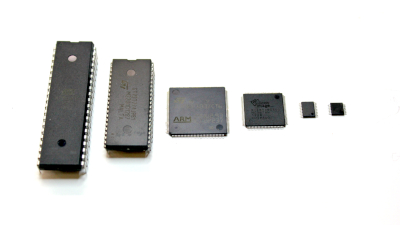 Like any product, an electronic or mechanical component has its lifespan at the end of which the
component is removed from the market. There are also many low-quality products on the market, so it
is important to choose a reliable supplier of components and evaluate possible alternatives to the
elemental base.
Like any product, an electronic or mechanical component has its lifespan at the end of which the
component is removed from the market. There are also many low-quality products on the market, so it
is important to choose a reliable supplier of components and evaluate possible alternatives to the
elemental base.
When looking for alternative solutions
- Potential end-of-life threats to components are assessed
- It is determined whether component parameters are redundant for a particular device node
- Alternatives with a better price-quality ratio are selected
- Reliable suppliers are selected who can provide quality components on time